Models
This section provides instructions for generating model instances in DiscretePOMP.jl.
Predefined models
The package includes a set of predefined models, which can be instantiated easily:
using DiscretePOMP # simulation / inference for epidemiological models
import Distributions # priors
model = generate_model("SIS", [100,1])Customising predefined models
DPOMPModels are mutable $structs$, which means that their properties can be altered after they have been instantiated. For example, we could specify a prior:
model.prior = Distributions.Product(Distributions.Uniform.(zeros(2), [0.01, 0.5]))Custom models from scratch
Models can also be specified manually. For example, the model we just created could also be instantiated like so:
# rate function
function sis_rf!(output, parameters::Array{Float64, 1}, population::Array{Int64, 1})
output[1] = parameters[1] * population[1] * population[2]
output[2] = parameters[2] * population[2]
end
# define obs function
function obs_fn(y::Observation, population::Array{Int64, 1}, theta::Array{Float64,1})
y.val .= population
end
# prior
prior = Distributions.Product(Distributions.Uniform.(zeros(2), [0.01, 0.05]))
# obs model
function si_gaussian(y::Observation, population::Array{Int64, 1}, theta::Array{Float64,1})
obs_err = 2
tmp1 = log(1 / (sqrt(2 * pi) * obs_err))
tmp2 = 2 * obs_err * obs_err
obs_diff = y.val[2] - population[2]
return tmp1 - ((obs_diff * obs_diff) / tmp2)
end
tm = [-1 1; 1 -1] # transition matrix
# define model
model = DPOMPModel("SIS", sis_rf!, [100, 1], tm, obs_fn, si_gaussian, prior, 0)Model directory
Here we provide a brief overview of predefined models available in the package.
Epidemiological models
SIR model
The canonical Kermack-McKendrick susceptible-infectious-recovered model is perhaps the best known example of state-space models used within the field of epidemiology.
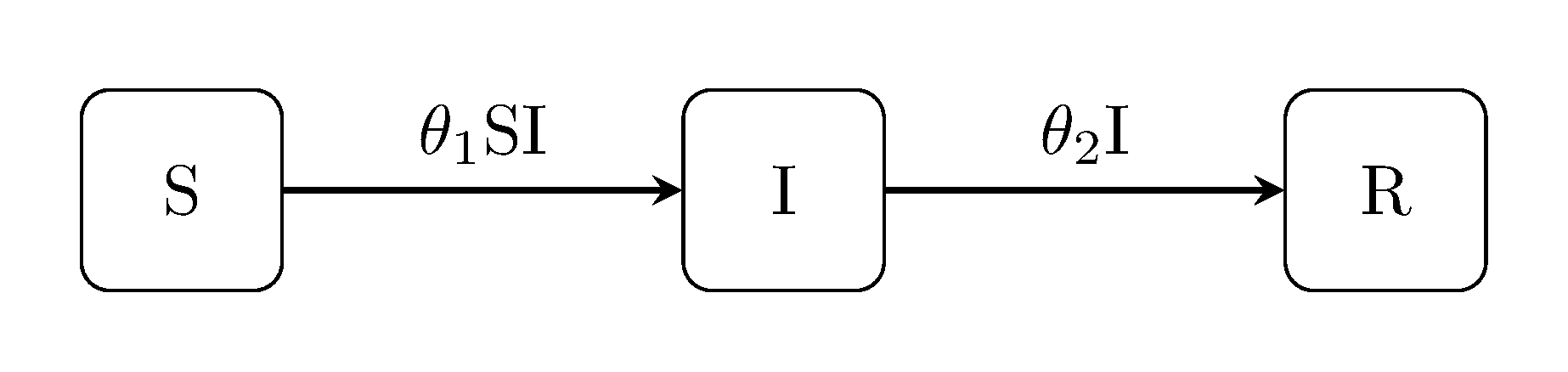
generate_model("SIR", [100, 1, 0])SI model
The susceptible-infectious model is the simplest conceptual example of this class of model; two states and only one type of event.
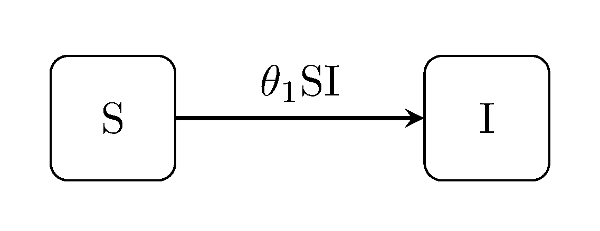
generate_model("SI", [100, 1])SIS model
Another common derivative of the SIR model.
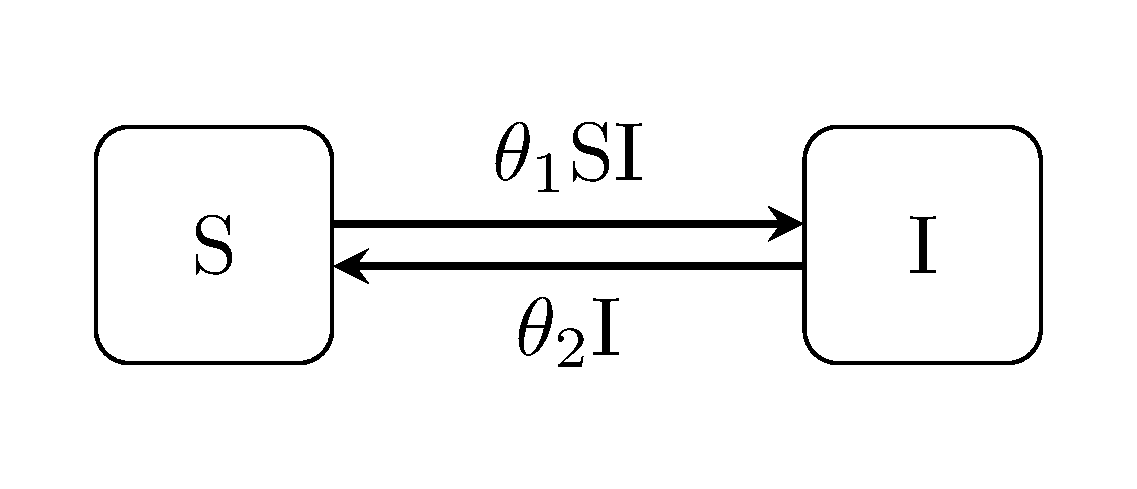
generate_model("SIS", [100, 1])SEI model
The SEI model includes an 'exposed' state, i.e. for modelling communicable diseases with latent non-infectious periods.
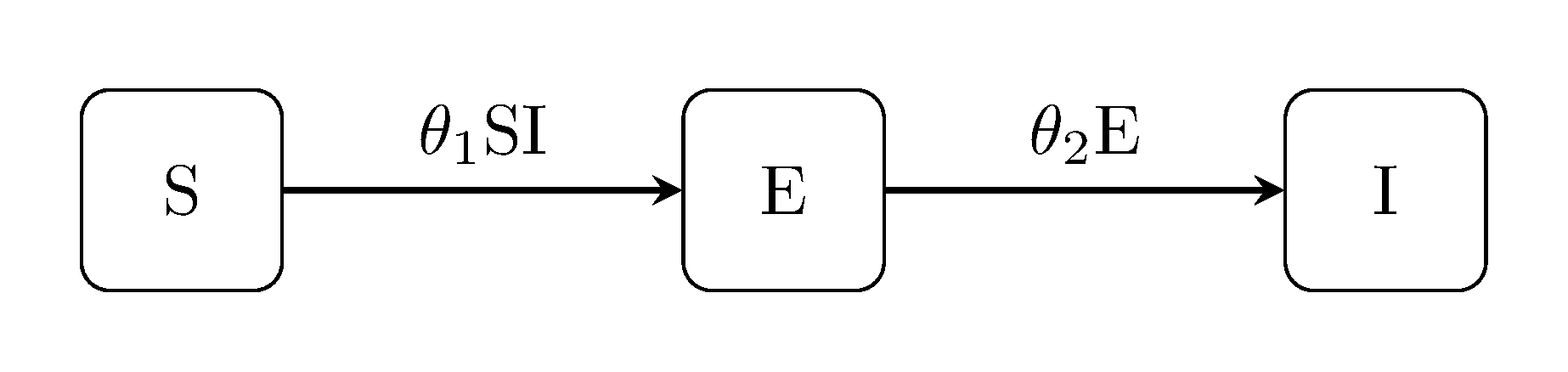
generate_model("SEI", [100, 0, 1])SEIR model
Somewhat obviously, the SEIR model concept combines the SEI with the SIR.
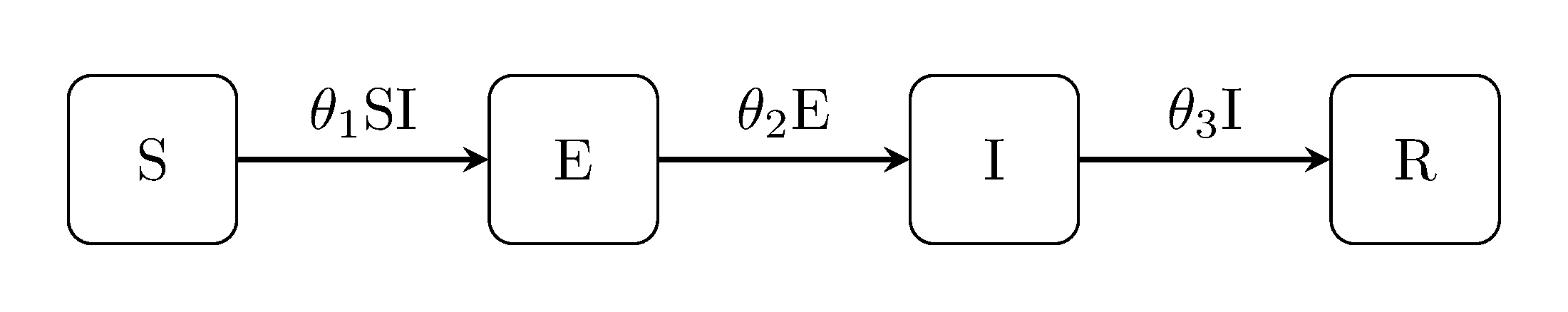
generate_model("SEIR", [100, 0, 1, 0])Others
The Lotka-Volterra predator-prey model
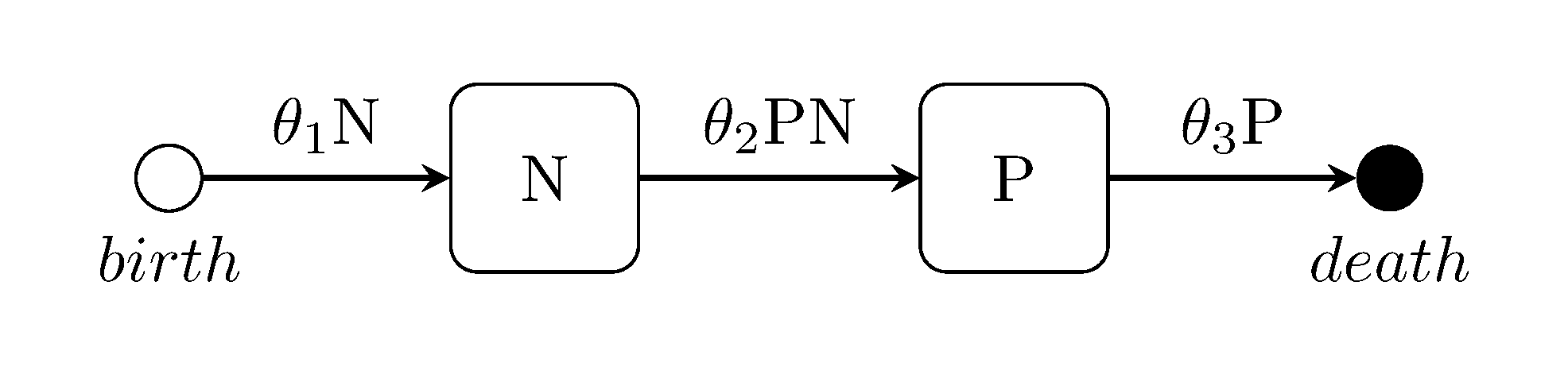
generate_model("LOTKA", [70, 70])Ross-MacDonald two-species Malaria model
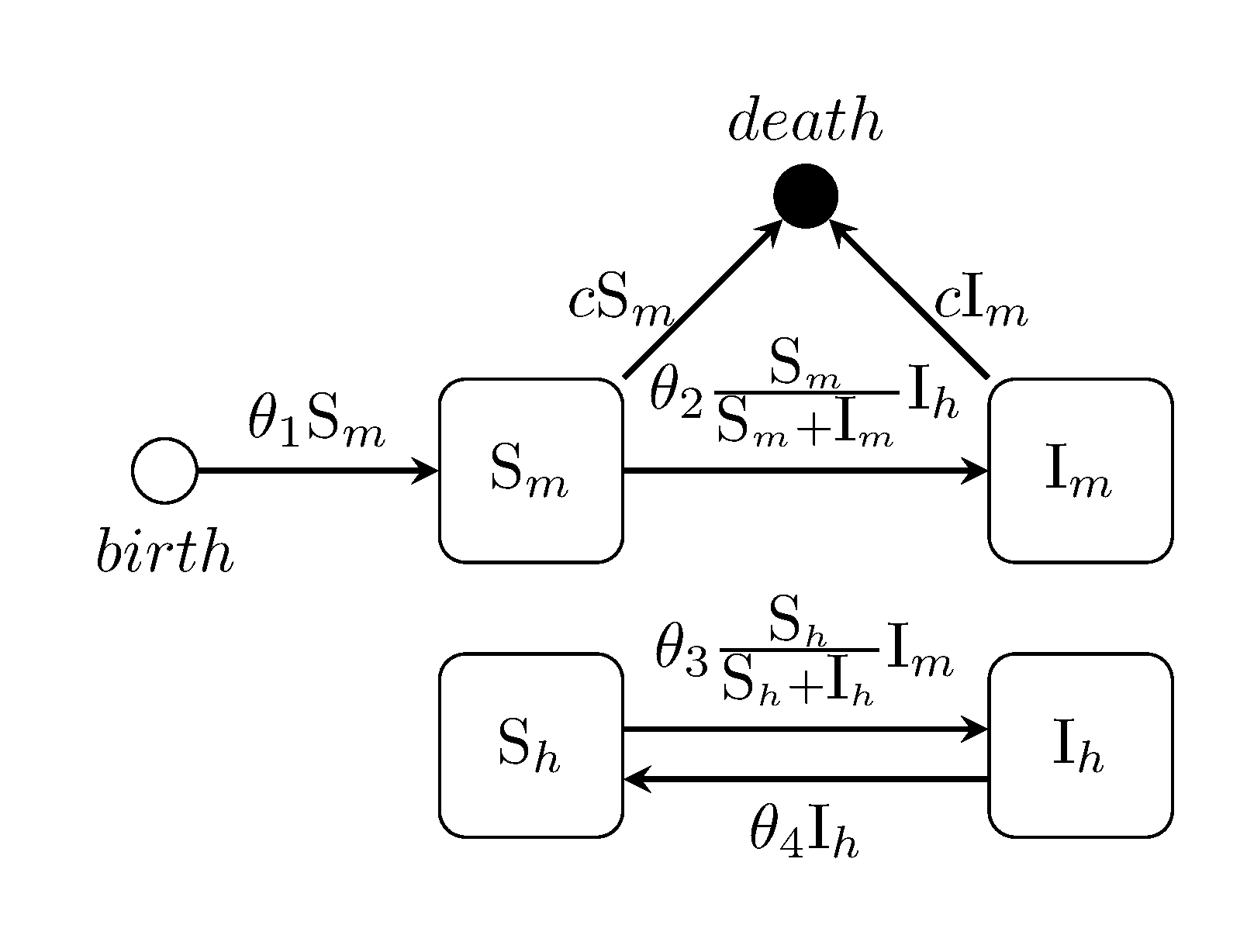
generate_model("ROSSMAC", [100, 0, 400, 50])